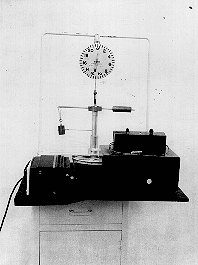

PURPOSE: To measure the centripetal force required to make a mass move in uniform circular motion.
DESCRIPTION: A one-kilogram mass is rotated at a constant angular velocity by a motor-driven pulley. The centripetal force is measured by passing the radial string holding the mass around a pulley (unseen in photograph) in the central tube and connecting it up the vertical tube to the spring scale. The angular velocity can be varied by rotating a knob on the front of the motor. The centripetal force can be calculated by measuring the angular velocity with a manual timer.
The dependence of the centripetal force on the square of the angular velocity can be shown as follows: Set the rotation speed of the motor so that the centripetal force is about 5 Newtons, and set a metronome to one beat per rotation. Using the metronome, double the rotation speed by speeding up the motor to two turns per metronome beat. The centripetal force will now read 20 Newtons, four times the original value.
SUGGESTIONS: Set motor speed knob to zero before turning device on.
REFERENCES: (PIRA 1D50.53)
EQUIPMENT: Pre-assembled rotator with timer and metronome.
SETUP TIME: None.
 |  |
 |  |
 |